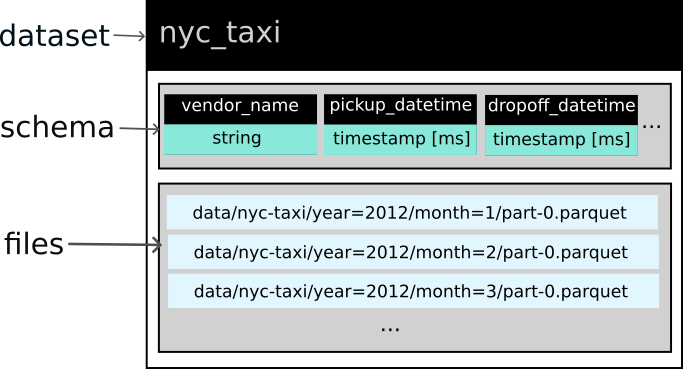
FileSystemDataset with 120 Parquet files
24 columns
vendor_name: string
pickup_datetime: timestamp[ms]
dropoff_datetime: timestamp[ms]
passenger_count: int64
trip_distance: double
pickup_longitude: double
pickup_latitude: double
rate_code: string
store_and_fwd: string
dropoff_longitude: double
dropoff_latitude: double
payment_type: string
fare_amount: double
extra: double
mta_tax: double
tip_amount: double
tolls_amount: double
total_amount: double
improvement_surcharge: double
congestion_surcharge: double
...
4 more columns
Use `schema()` to see entire schemaData Manipulation—Part 1
Goals
Avoiding these! But…don’t worry!
An Arrow Dataset
Arrow Datasets
Constructing queries
arrow dplyr queries
- query has been constructed but not evaluated
- nothing has been pulled into memory
Running the query
collect()evaluates the query, in-memory output returns to R
collect()
# A tibble: 10 × 4
year all_trips shared_trips pct_shared
<int> <int> <int> <dbl>
1 2012 178544324 53313752 29.9
2 2013 173179759 51215013 29.6
3 2014 165114361 48816505 29.6
4 2015 146112989 43081091 29.5
5 2016 131165043 38163870 29.1
6 2017 113495512 32296166 28.5
7 2018 102797401 28796633 28.0
8 2019 84393604 23515989 27.9
9 2020 24647055 5837960 23.7
10 2021 30902618 7221844 23.4Calling nrow() to see how much data
Your Turn
Use the function nrow() to work out the answers to these questions:
- How many taxi fares in the dataset had a total amount greater than $100?
Previewing output for large queries
How much were fares in GBP (£)?
How many rows?
Use head() and collect() to preview results
Use across() to transform data in multiple columns
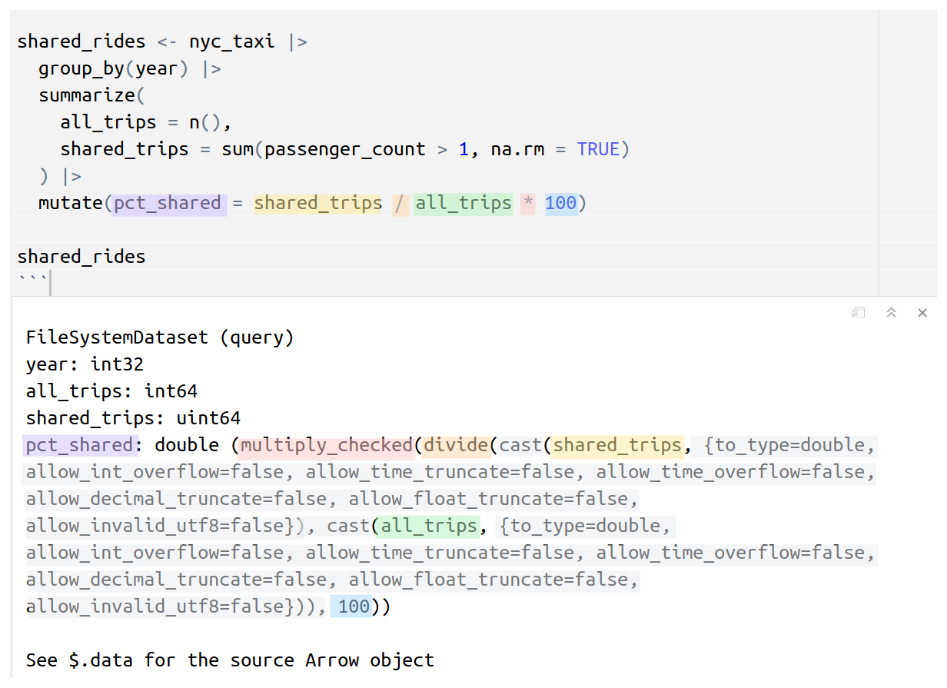
nyc_taxi |>
mutate(across(ends_with("amount"), list(pounds = ~.x * 0.79))) |>
select(contains("amount")) |>
head() |>
collect()# A tibble: 6 × 8
fare_amount tip_amount tolls_amount total_amount fare_amount_pounds
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 29.7 6.04 0 36.2 23.5
2 9.3 0 0 9.8 7.35
3 4.1 1.38 0 5.98 3.24
4 4.5 1 0 6 3.56
5 4.5 0 0 5.5 3.56
6 4.1 0 0 5.6 3.24
# ℹ 3 more variables: tip_amount_pounds <dbl>, tolls_amount_pounds <dbl>,
# total_amount_pounds <dbl>Summary
- Use
nrow()to work out how many rows of data your analyses will return - Use
collect()to pull all of the data into your R session - Use
head()andcollect()to preview results - Use
across()to manipulate data in multiple columns at once
dplyr verbs API in arrow - alternatives
Example - slice()
First three trips in the dataset in 2021 where distance > 100 miles
Head to the docs!
or view them at https://arrow.apache.org/docs/r/reference/acero.html
A different function
Or call collect() first
tidyr functions - pivot
duckdb
- in-memory database
- columnar
- understands Arrow format
sharing data with duckdb and arrow
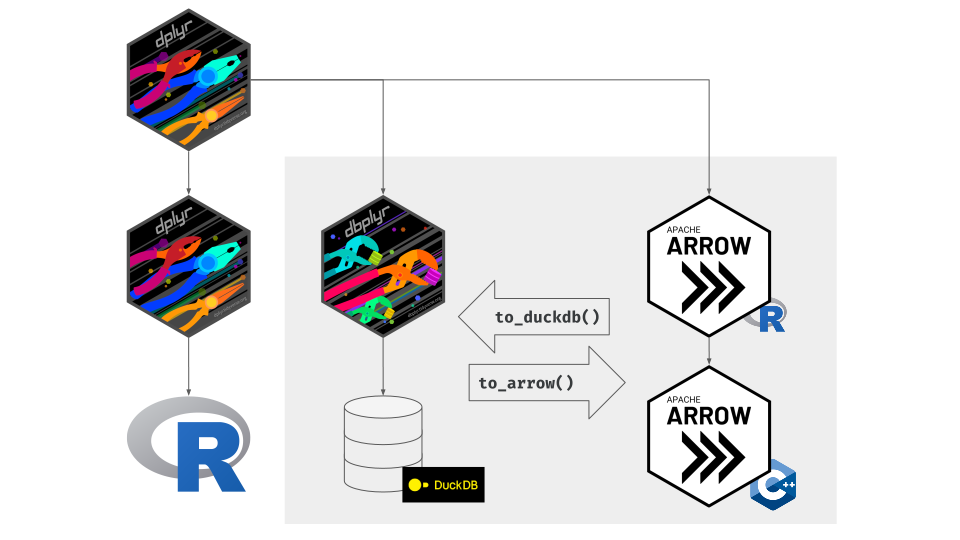
tidyr functions - pivot with duckdb!
library(duckdb)
nyc_taxi |>
group_by(vendor_name) |>
summarise(max_fare = max(fare_amount)) |>
to_duckdb() |> # send data to duckdb
pivot_longer(!vendor_name, names_to = "metric") |>
to_arrow() |> # return data back to arrow
collect()# A tibble: 3 × 3
vendor_name metric value
<chr> <chr> <dbl>
1 CMT max_fare 998310.
2 VTS max_fare 10000.
3 <NA> max_fare 3555.Using functions inside verbs
Using functions inside verbs
Morning vs afternoon with namespacing
Morning vs afternoon - without namespacing
How does this work?
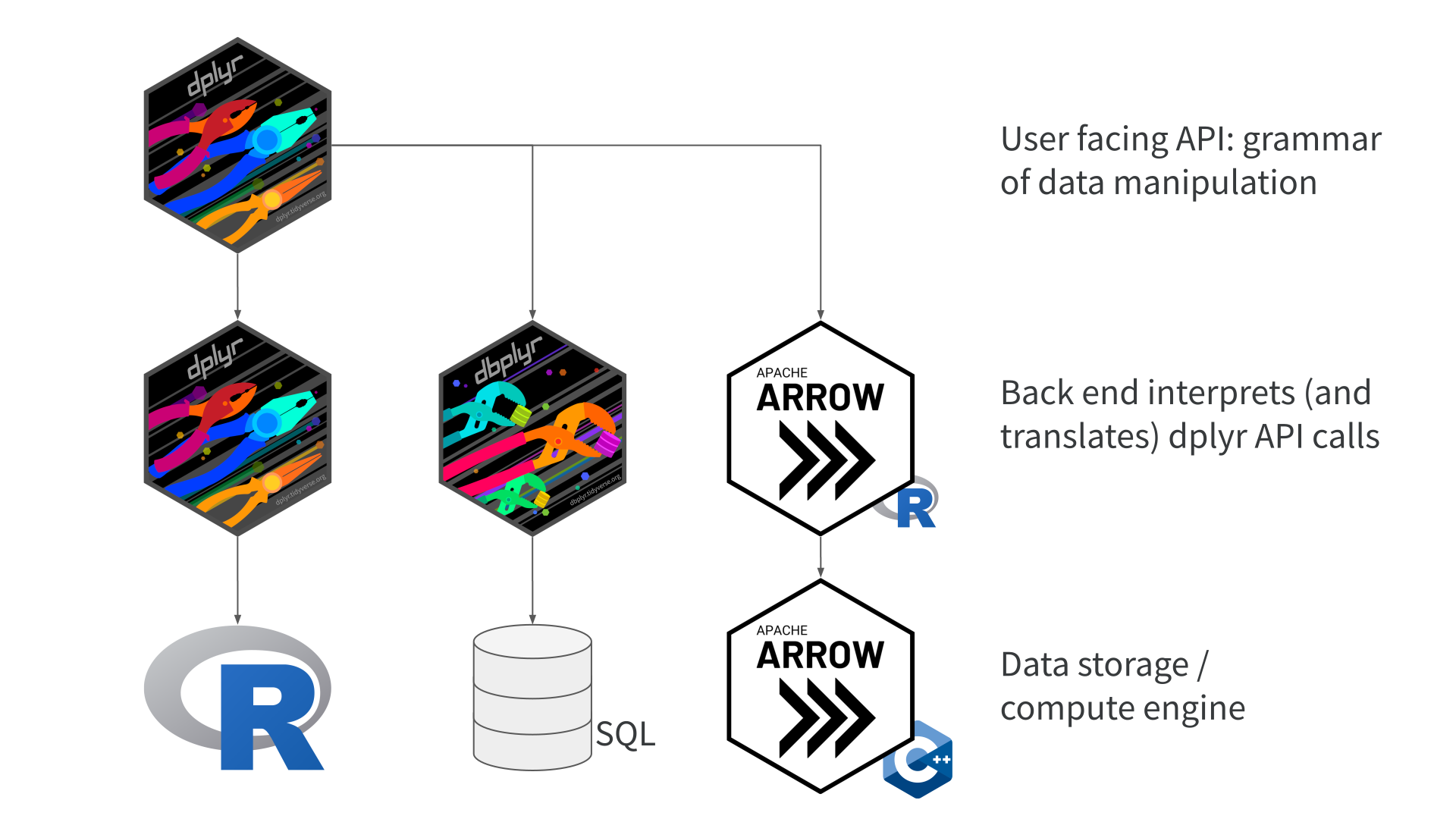 ## Acero
## Acero
- arrow’s query execution engine
- use Arrow functions on Arrow Datasets
Acero
arrow dplyr queries
What if a function isn’t implemented?
Head to the docs again to see what’s implemented!
or view them at https://arrow.apache.org/docs/r/reference/acero.html
Option 1 - find a workaround!
nyc_taxi |>
mutate(vendor_name = ifelse(vendor_name == "CMT", NA, vendor_name)) |>
head() |>
collect()# A tibble: 6 × 24
vendor_name pickup_datetime dropoff_datetime passenger_count
<chr> <dttm> <dttm> <int>
1 <NA> 2012-01-20 06:09:36 2012-01-20 06:42:25 1
2 <NA> 2012-01-20 06:54:10 2012-01-20 07:06:55 1
3 <NA> 2012-01-20 00:08:01 2012-01-20 00:11:02 1
4 <NA> 2012-01-20 00:36:22 2012-01-20 00:39:44 1
5 <NA> 2012-01-20 12:58:32 2012-01-20 13:03:04 1
6 <NA> 2012-01-20 11:40:20 2012-01-20 11:43:43 2
# ℹ 20 more variables: trip_distance <dbl>, pickup_longitude <dbl>,
# pickup_latitude <dbl>, rate_code <chr>, store_and_fwd <chr>,
# dropoff_longitude <dbl>, dropoff_latitude <dbl>, payment_type <chr>,
# fare_amount <dbl>, extra <dbl>, mta_tax <dbl>, tip_amount <dbl>,
# tolls_amount <dbl>, total_amount <dbl>, improvement_surcharge <dbl>,
# congestion_surcharge <dbl>, pickup_location_id <int>,
# dropoff_location_id <int>, year <int>, month <int>Option 2
- In data manipulation part 2!
Your Turn
Use the
dplyr::filter()andstringr::str_ends()functions to return a subset of the data which is a) from September 2020, and b) the value invendor_nameends with the letter “S”.Try to use the
stringrfunctionstr_replace_na()to replace anyNAvalues in thevendor_namecolumn with the string “No vendor” instead. What happens, and why?Bonus question: see if you can find a different way of completing the task in question 2.
Working with custom functions
Arrow 17.0.0 or later!
# A tibble: 6 × 2
pickup_datetime pickup_text
<dttm> <chr>
1 2012-01-08 12:50:38 Sunday PM
2 2012-01-08 12:52:01 Sunday PM
3 2012-01-07 18:39:26 Sunday AM
4 2012-01-07 18:40:49 Sunday AM
5 2012-01-08 19:42:37 Monday AM
6 2012-01-08 12:51:47 Sunday PM How did that work?
Custom function converted to Arrow Expression; query doesn’t contain any reference to the time_text() function.
FileSystemDataset (query)
pickup_datetime: timestamp[ms]
pickup_text: string (binary_join_element_wise(cast(strftime(pickup_datetime, {format="%A"}), {to_type=string, allow_int_overflow=false, allow_time_truncate=false, allow_time_overflow=false, allow_decimal_truncate=false, allow_float_truncate=false, allow_invalid_utf8=false}), cast(if_else((hour(pickup_datetime) < 12), "AM", "PM"), {to_type=string, allow_int_overflow=false, allow_time_truncate=false, allow_time_overflow=false, allow_decimal_truncate=false, allow_float_truncate=false, allow_invalid_utf8=false}), " ", {null_handling=REPLACE, null_replacement="NA"}))
See $.data for the source Arrow objectAnything else to be aware of?
- arrow 17.0.0 or later
- this will only work for functions which have Arrow bindings
- use
?aceroto see which ones do
Summary
- Working with Arrow Datasets allow you to manipulate data which is larger-than-memory
- You can use many dplyr functions with arrow - run
?aceroto view the docs - You can pass data to duckdb to use functions implemented in duckdb but not arrow
